Blood Oxygen Level; all you need to know:
/0 Comments/in Health, Health and wellness tip, Respiratory /by Rachel MataWhat is Blood Oxygen Level?
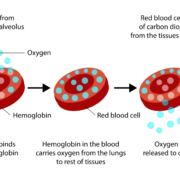
Blood oxygen level measures the oxygen circulating in your blood. Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s parts, indicating how effectively the body moves oxygen from the lungs to the cells. This level is crucial for health.
Measuring Your Blood Oxygen Level
You can measure your blood oxygen level in two ways: through an arterial blood gas test or a pulse oximeter. The arterial blood gas test, a blood test, accurately measures your blood’s oxygen level and checks your blood’s pH balance. Although accurate, this test is invasive. On the other hand, a pulse oximeter offers a noninvasive estimate by sending infrared light into capillaries in your finger, toe, or earlobe and measuring the reflected light. This method provides a reading of your blood’s oxygen saturation (SpO2 level) but has a 2 percent error margin. Despite being slightly less precise, doctors prefer it for its convenience in offering quick readings.
How Blood Becomes Oxygenated
Oxygen saturation in blood starts in the lungs’ alveoli, tiny air sacs responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules with the bloodstream. The Oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the blood, which then delivers oxygen to tissues while carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs. Ideally, oxygen levels in your blood depend on several factors, including the amount of inhaled oxygen, alveoli efficiency, hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells, and hemoglobin’s oxygen attraction. Usually, hemoglobin carries enough oxygen for the body’s needs, but certain diseases can impair its ability to bind oxygen.
Low Blood Oxygen Levels
An oxygen saturation level below 95% is generally abnormal, and below 90% signals an emergency requiring oxygen therapy. The brain, highly sensitive to hypoxia, can suffer cell death within five minutes of oxygen deprivation, leading to serious outcomes like coma, seizures, and brain death if prolonged. Identifying and addressing the cause of low oxygen saturation is crucial. Conditions like COPD and asthma typically result from inadequate air exchange in the lungs and alveoli. Treatments may include oxygen therapy, steroids, or bronchodilators to open the airways.
Treatment
For low blood oxygen levels, treatment options include supplemental oxygen, available in-office or for home use, though some devices require a prescription. Lifestyle changes, like a healthy diet, can also improve oxygen levels and overall health. Since iron deficiency often leads to low oxygen saturation, consuming iron-rich foods such as meat, fish, kidney beans, lentils, and cashew nuts is beneficial.
Disclaimer
This information aims to enhance understanding and knowledge of health topics and is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions about a medical condition or treatment. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it based on what you have read on this website.
References:
A Guide to Healthy Living for Seniors
/0 Comments/in Health, Health and wellness tip /by Rachel MataWhat is Healthy Living for Seniors
As you grow older, you go through many changes, and you may need to adjust your lifestyle for healthy aging. Our minds and bodies undergo a wide variety of mental, emotional, and physical changes. While some aspects of life may become more difficult, active living for older adults is still well within reach. In this guide to healthy living for seniors, we’ll explore the many ways you can live a full, satisfying life well into your golden years. Healthy eating and regular physical activity can be keys to good health at any age. Making suitable lifestyle choices may also prevent some health problems, such as diabetes, heart disease, and some cancers.
What foods should seniors avoid?
Food plays a central role in all of our lives. Eating is both a way to sustain ourselves and an important part of our culture. People often mark major life events with a large feast from wedding cakes to birthday cakes, beautiful holiday spreads with family to casual lunches with friends. As adults age, they need fewer total calories, but higher amounts of some nutrients, especially calcium and vitamin D. In terms of nutrition, you need to focus on quality, not quantity. For both optimal physical and mental health, older adults truly need to make every calorie count.
Here are foods that you should cut down on (or avoid eating altogether) as you get older, and why:
- Raw or undercooked eggs, meat, and poultry.
Undercooked foods such as eggs, meat, poultry, and sushi can cause food poisoning, which can trigger sepsis and septic shock. Although anyone can develop infection and sepsis, seniors are at higher risk.
- High-sodium foods.
Too much salt can be a problem for older adults, especially if you have a history of hypertension. If your food is lacking flavor, try adding different types of herbs and spices rather than loading up with table salt. Additionally, always review the sodium content on nutritional labels.
- Caffeine.
Caffeine not only keeps many people from getting a good night’s sleep, but it may also increase anxiety and make your heart beat more quickly or irregularly. This could be dangerous if you have a heart condition. Caffeine can also be found in many teas, some sodas, chocolate, and even some medications, including over-the-counter pain killers.
- Sodas and sugary drinks.
Excess sugar also leads to obesity and other health issues. An ice-cold cola may seem tempting if you’re hot and thirsty, but sodas and many sports drinks contain a large amount of sugar. A cola can contain 39 grams of sugar in one 12-ounce serving, the equivalent of almost 10 teaspoons of sugar! If you have prediabetes, regular consumption of these types of drinks may raise your blood sugar to a diagnosis of diabetes.
- Alcoholic beverages.
Enjoying an occasional alcoholic beverage is harmless for many people. However, if you live with a chronic illness, such as diabetes, or you take certain types of medications, such as antihistamines, painkillers (analgesics), and medications for hypertension (high blood pressure), alcohol should be avoided.
Why is keeping a healthy weight important?
Aim for a stable weight as you get older. People of all ages need protein for strong, healthy bodies. Some older adults do not get the protein they need to maintain muscle mass, fight infection and recover from an accident or surgery. Keeping a healthy weight may help improve your health. The weight that is healthiest for you may be higher than that of a younger person. Ask your health care professional what a healthy weight for you may be.
Sometimes older adults feel lonely, sad, low, or stressed because of life changes, loss of loved ones, health problems, caring for other family members, or financial issues. Being good to yourself may help you improve your lifestyle habits, your “get up and go,” and your ability to cope with the demands of daily living.
Here are some ideas for being good to yourself
- Stay in touch with family, friends, or former coworkers to stay engaged and to keep your spirits up.
- See your health care professional regularly and share any concerns.
- Get enough sleep.
- Join a walking group or another social group.
- If you are retired, pursue a new hobby or volunteer to help keep you active and social.
- Surround yourself with people you enjoy.
Remember, it’s never too late to improve your eating habits, become more physically active, and be good to yourself for a healthier life. Strengthening your immune system and staying active can keep you healthier and make you less susceptible to illnesses throughout the year. You are never too old to enjoy the benefits of improved nutrition and fitness. With nutrient-rich foods and activities with friends, you can feel an immediate difference in your energy levels and enjoyment of life. In fact, as we get older, our food and activity choices become even more important to our health.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
https://www.healthline.com/health/flu/boost-immune-system-over-65#quit-smoking
What are the symptoms of low oxygen levels?
/0 Comments/in Health, Health and wellness tip, Respiratory /by Rachel MataWhat is Blood Oxygen Level?
Blood oxygen level is a crucial measure indicating the amount of oxygen circulating in our blood. Essentially, red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s various parts. Interestingly, too little or too much oxygen can have serious health consequences. Therefore, it’s vital to seek immediate medical care if blood oxygen levels fall significantly. Similarly to how we monitor blood pressure or blood sugar, keeping an optimal blood oxygen level is essential for maintaining good health.
What Should Your Oxygen Level Be?
Under normal conditions, oxygen saturation levels should range between 95% to 100%. If levels fall below this range, one must consult a doctor. Moreover, oxygen levels between 91% and 95% might indicate an underlying condition, urging immediate medical consultation. Notably, a level below 90% signals a medical emergency, known as hypoxemia, requiring urgent care. Furthermore, if oxygen saturation dips below 85%, it severely affects the brain, potentially leading to vision changes and loss of consciousness. Alarmingly, levels below 80% impact the brain, liver, and other vital organs significantly. Lastly, cyanosis, which indicates a saturation below 67%, presents as a bluish tinge on the skin or mucous membranes due to insufficient oxygen.
Symptoms of Low Oxygen Levels
Interestingly, hypoxemia, or the condition of having unusually low blood oxygen, triggers a variety of symptoms that can vary significantly from person to person depending on how low the oxygen level is. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, headaches, restlessness, dizziness, rapid breathing, chest pain, confusion, high blood pressure, lack of coordination, visual disorders, a sense of euphoria, and a rapid heartbeat. Furthermore, extremely low levels lead to cyanosis, which is marked by a bluish discoloration of the skin around the lips and fingernails.
Preventing Low Oxygen Levels
Fortunately, with the right medical advice combined with specific changes in lifestyle and food habits, we can maintain appropriate blood oxygen levels and prevent them from getting too low. Healthcare workers recommend adopting a nutritious diet, considering yoga and breathing exercises, exercising regularly, using preventive medications such as inhalers, and avoiding triggers that may cause breathing difficulties. Additionally, keeping yourself hydrated, stopping smoking, and avoiding secondhand smoke are crucial steps. Treating the underlying condition responsible usually improves blood oxygen levels. For individuals living with chronic lung diseases or those who have contracted COVID-19, regular blood oxygen monitoring might be necessary. Adopting lifestyle changes, in conjunction with oxygen therapy, could significantly help raise their oxygen saturation levels. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are the keys to avoiding complications and ensuring good health. Therefore, booking an appointment with specialists in the field to get the right medical advice is highly recommended.
Disclaimer
This information serves to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. Importantly, it is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment. Moreover, never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
Anxiety During Pregnancy
/0 Comments/in Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Personal, Pregnancy, Pregnancy Problem /by Rachel MataWhat is Anxiety?
Anxiety is feelings of worry, stress, or fear, and is a normal part of life. Anxiety is not only part of being pregnant, it’s part of being human. We all worry, and pregnancy can often amplify those worries. Antenatal anxiety is a very common experience. More than 1 in 10 women experience anxiety at some point during their pregnancy.
Pregnancy can be an incredibly wonderful time in your life, as well as a very scary time in your life. Pregnancy brings a mix of feelings, and not all of them are good. Your whole life as well as your body is going through a number of changes. These changes can be especially anxiety-provoking if this is your first pregnancy. You want everything to go perfectly, but you find yourself struggling with an array of worries and fears about every possible thing that could go wrong. If you’re feeling worried, you’re not alone. Worry is common, especially during a woman’s first pregnancy or an unplanned one. It can be even harder if you’re dealing with depression or anxiety. The more you think about those things, the worse your anxiety becomes.
What causes anxiety during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is also a time of tremendous change and hormonal changes during pregnancy may affect the chemicals in your brain. This can cause anxiety. After all, not everything that makes you feel anxious is under your control. Some of these feelings and sensations are welcomed, while others are downright uncomfortable and scary. You may even have complications or other issues that arise that keep you up at night.
What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety During Pregnancy?
Since there are different types of anxiety disorders, the symptoms vary. Speak with your doctor about any symptoms you experience so he or she can accurately diagnose and treat you. Some common symptoms of anxiety disorders include:
- feeling an uncontrollable sense of anxiousness
- worrying excessively about things, especially your health or baby
- feeling irritable or agitated
- having tense muscles
- Feeling nervous, anxious or on edge frequently
- Finding it difficult or impossible to relax
- Feeling restless and hard to stay still
- Feeling afraid, or thinking that bad things will happen
- Inability to concentrate
- Difficulty sleeping
Things You Can Do to Manage Your Anxiety
- Avoid Scary Stories and Images
- Stop Thinking of “What Ifs”
- Meditate
- Deep-breathing exercises
- Avoid Stress
- Find a release
- Talk about it
- Rest up
Treatment for Anxiety During Pregnancy
- Counseling or therapy
- Support groups
- Medication
- Other approaches
- Exercise
- Eating a healthy diet
- Get enough sleep
- Meditate and breathe
When to See a Doctor?
Even if you experience only mild symptoms of anxiety, it is important to inform your doctor. If your anxiety is affecting your daily life or if you’re having frequent panic attacks, you should call your doctor right away. Only they can diagnose you with an anxiety disorder and recommend the best, most effective treatment options for you. Seeking help is the best step you can take to ensure that you and your child stay safe and healthy. The sooner you get help, the sooner you’ll be able to gain peace of mind for your health and the health of your growing baby.
Always remember; Take care of yourself as much as you can, for your and your baby’s health. Be sure to eat well, exercise, get enough sleep, and take your prenatal vitamins. Look for ways to reduce your stress.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/anxiety-coping-tips#treatment
Foods to Eat and Avoid During Pregnancy
/0 Comments/in Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Pregnancy /by Rachel MataFoods to Eat and Avoid During Pregnancy
It’s well known that a mother’s diet during pregnancy is very important to the health of her baby. Expecting mothers need to consume more vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that are helpful for a fetus’s growth and development. However, there are also some foods pregnant women should avoid. There are some foods you should not eat when you’re pregnant because they might make you ill or harm your baby. Certain foods should only be consumed rarely, while others should be avoided completely. Make sure you know the important facts about which foods you should avoid or take extra care with when you’re pregnant. The best foods to eat are freshly cooked or freshly prepared food.

5 foods to eat during pregnancy
- Produce containing Vitamin C, like oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli, support the baby’s growth and improves iron absorption. Adding in servings of green veggies is an efficient way to pack in vitamins and fend off constipation due to all that fiber. Vegetables rich diets linked means reduced risk of low birth weight.
- Foods that have iron, such as beans, lentils, green leafy vegetables, Lean beef, pork, chicken, and spinach are excellent sources of high-quality protein and all support the mother’s body in making more blood for both mom and baby. Red blood cells use iron as a part of hemoglobin, an essential mineral.
- Dairy products. During pregnancy, you need to consume extra protein and calcium to meet the needs of your growing little one. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt should be on the docket. Foods rich in calcium, including pasteurized dairy products (yogurt, cow’s milk, and hard cheeses) as well as almonds, broccoli, and garbanzo beans will help support the development of bones and teeth. Dairy products contain two types of high-quality protein: casein and whey. Dairy is the best dietary source of calcium and provides high amounts of phosphorus, B vitamins, magnesium, and zinc.
- Foods containing Omega-3 fatty acids (EHA and DHA) such as sardines, salmon, trout, and canned light tuna. Or choose a prenatal supplement with Omega-3s if you don’t like fish.
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated supports the proper delivery of nutrients through the blood to the baby. Increasing your water intake may also help relieve constipation and reduce your risk of urinary tract infections, which are common during pregnancy. We all have to stay hydrated and pregnant especially. During pregnancy, blood volume increases by about 45 percent. General guidelines recommend that pregnant women drink about 80 ounces (2.3 liters) of water daily. But the amount you really need varies. Check with your doctor for a recommendation based on your specific needs.

5 foods to avoid during pregnancy
- Anything containing unpasteurized milk, however, is a no-no. These products could lead to foodborne illness. Avoid soft cheeses, such as brie, feta, and blue cheese, unless they are clearly labeled as being pasteurized or made with pasteurized milk. Also, avoid drinking unpasteurized juice.
- Any food in a dented can increases the risk for botulism, a foodborne illness that can cause neuromuscular deficits for expecting mothers.
- Avoid raw, undercooked, or contaminated seafood. Consuming raw seafood, like sushi or raw oysters, increases the risk of salmonella, a foodborne illness that can cause fever and nausea, vomiting, stomach cramping, and diarrhea for pregnant women, as well as intrauterine sepsis that can affect babies.
- Avoid seafood high in mercury. Fish with a high mercury content, such as swordfish, shark, orange roughy, marlin, and king mackerel. Too much mercury could harm your baby’s developing nervous system
- Avoid Alcohol during pregnancy. There is nothing as safe level of alchol during pregnancy. The safest bet is to avoid alcohol entirely. Drinking alcohol during pregnancy leads to a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Drinking alcohol may also result in fetal alcohol syndrome, which can cause facial deformities and intellectual disability.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
Headaches During Pregnancy
/0 Comments/in Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Pregnancy, Pregnancy Problem /by Rachel MataHeadaches during pregnancy
If you’re pregnant, you’re no doubt experiencing new aches and pains. Headaches can be common in early pregnancy. They usually improve as your pregnancy goes on. Headaches in women can often be triggered by a change in hormones during pregnancy. Expectant mothers may experience an increase or decrease in the number of headaches. A headache can sometimes be a symptom of pre-eclampsia, which can lead to serious complications if it’s not monitored and treated. Pre-eclampsia usually starts after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Nearly all women have occasional headaches, but having a headache in pregnancy is not fun, especially tricky in the first trimester when you should avoid many medicines. Whether your headache is from tension or is a full-blown migraine, there are some things you should know.
What causes headaches during pregnancy?
The exact cause of a headache isn’t always clear. In the first trimester, changing hormone levels and blood volume may play a role. Hunger and low levels of blood sugar can trigger headaches, too. Researchers believe that overly excited brain cells stimulate a release of chemicals. These chemicals irritate blood vessels on the brain’s surface. That, in turn, causes blood vessels to swell and stimulate the pain response. Headaches during your second or third trimester of pregnancy may be a sign that you have high blood pressure. About 6 to 8 percent of pregnant women ages 20 to 44 in the United States have high blood pressure.
Other causes of headaches during pregnancy can include:
- not getting enough sleep
- hormonal changes
- withdrawal from caffeine (e.g. in coffee, tea, or cola drinks)
- low blood sugar
- dehydration
- feeling stressed
- poor posture, particularly as your baby gets bigger
- having depression or anxiety
- weight changes
- high blood pressure
Types of headaches
Most headaches during pregnancy are primary headaches. This means that the headache pain happens by itself. It’s not a sign or symptom of another disorder or a complication in the pregnancy. Primary headaches include:
- Tension headaches: A tension-type headache (TTH) is generally a mild to moderate pain that’s often described as feeling like a tight band around the head. About 26 percent of headaches during pregnancy are tension headaches and are common in the first trimester of your pregnancy.
- Migraine attacks: Migraine headaches are a common type of headache in pregnancy. These painful, throbbing headaches are usually felt on one side of the head and result from the expansion of the blood vessels in the brain.
- Cluster headaches: Cluster headaches are one of the most painful types of headaches. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head.
What can I do about headaches?
Steps to manage headaches include the following:
- Avoid any known headache triggers
- Include physical activity in your daily routine.
- Reduce your stress level and relax
- Practice relaxation techniques.
- Eat regularly
- Follow a regular sleep schedule.
- drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration
- get enough sleep
Treatment for headaches during pregnancy
If you experience frequent headaches that don’t go away with paracetamol, it could be a sign of a more serious medical condition called pre-eclampsia. Most pregnant women can safely take acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) to treat occasional headaches. Talk to your doctor before taking your regular headache pain medication during pregnancy.
See your doctor if you have any headache pain at all during pregnancy. Get urgent medical attention if you have a fever, severe pain, and blurred vision. Let your doctor know right away.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/headache-during-pregnancy#treatment
https://www.webmd.com/migraines-headaches/migraines-headaches-finding-help
Stages of Pregnancy
/0 Comments/in Child birth, Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Pregnancy /by Rachel MataStages of Pregnancy
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg that will become your baby rapidly divides into many cells. By the eighth week of pregnancy, the embryo develops into a fetus. Pregnancy is counted as 40 weeks, starting from the first day of the mother’s last menstrual period. These weeks are divided into three trimesters. Your estimated date of birth is only to give you a guide. Babies come when they are ready and you need to be patient. Below we explore the stafes of pregnancy:
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters:
- First trimester – conception to 12 weeks
- Second trimester – 12 to 24 weeks
- Third trimester – 24 to 40 weeks.
The moment of conception is when the woman’s ovum (egg) is fertilized by the man’s sperm to complete the genetic make-up of a human fetus. At this moment (conception), the sex and genetic make-up of the fetus begin. About three days later, the fertilized egg cell divides rapidly and then passes through the Fallopian tube into the uterus, where it attaches to the uterine wall. The attachment site provides nourishment to the rapidly developing fetus and becomes the placenta.
The start of Stages of Pregnancy?
Medical professionals measure pregnancy week 1 from the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age, or menstrual age. It’s about two weeks ahead of when conception actually occurs. Although a woman is not actually pregnant at this point, counting week 1 from the last menstrual period can help determine a woman’s estimated pregnancy due date. Your healthcare provider will ask you about this date and will use it to figure out how far along you are in your pregnancy.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
From the moment of conception, the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be present in your blood. This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. While you may get a positive POAS test at 3 weeks, it’s a good idea to wait a week or two and test again to confirm. A blood test also can detect hCG and is more sensitive than a urine test. Pregnancy can detect pregnancy as early as 6 days after ovulation, you could be able to confirm your pregnancy at/around 3 weeks.
Stages of Fetal Development
During the first trimester, your body undergoes many changes. Hormonal changes affect almost every organ system in your body. These changes can trigger symptoms even in the very first weeks of pregnancy. Your period stopping is a clear sign that you are pregnant.
The developing baby is tinier than a grain of rice. The rapidly dividing cells are in the process of forming the various body systems, including the digestive system. The evolving neural tube will eventually become the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
First trimester (week 1–week 12)
- 1 and 2: Getting ready
- 3: Fertilization
- 4: Implantation
- 5: Hormone levels increase
- 6: The neural tube closes
- 7: Baby’s head develops
- 8: Baby’s nose forms
- 9: Baby’s toes appear
- 10: Baby’s elbows bend
- 11: Baby’s genitals develop
- 12: Baby’s fingernails form
Second trimester (week 13–week 27)
Most women find this second trimester easier than the first. But it is just as important to stay informed during all stages of pregnancy.
You might notice that symptoms like nausea and fatigue are going away. But other new, more noticeable changes to your body are now happening. Your abdomen will expand as the baby continues to grow. And before this trimester is over, you will feel your baby beginning to move. Fetal development takes on new meaning in the second trimester. Highlights might include finding out your baby’s sex and feeling your baby move.
- 13: Urine forms
- 14: Baby’s sex becomes apparent
- 15: Baby’s scalp pattern develops
- 16: Baby’s eyes move
- 17: Baby’s toenails develop
- 18: Baby begins to hear
- 19: Baby develops a protective coating
- 20: The halfway point
- 21: Baby can suck his or her thumb
- 22: Baby’s hair becomes visible
- 23: Fingerprints and footprints form
- 24: Baby’s skin is wrinkled
- 25: Baby responds to your voice
- 26: Baby’s lungs develop
- 27: At 27 weeks, or 25 weeks after conception, your baby’s nervous system is continuing to mature. Your baby is also gaining fat, which will help his or her skin look smoother.
Third trimester (week 28–week 40)
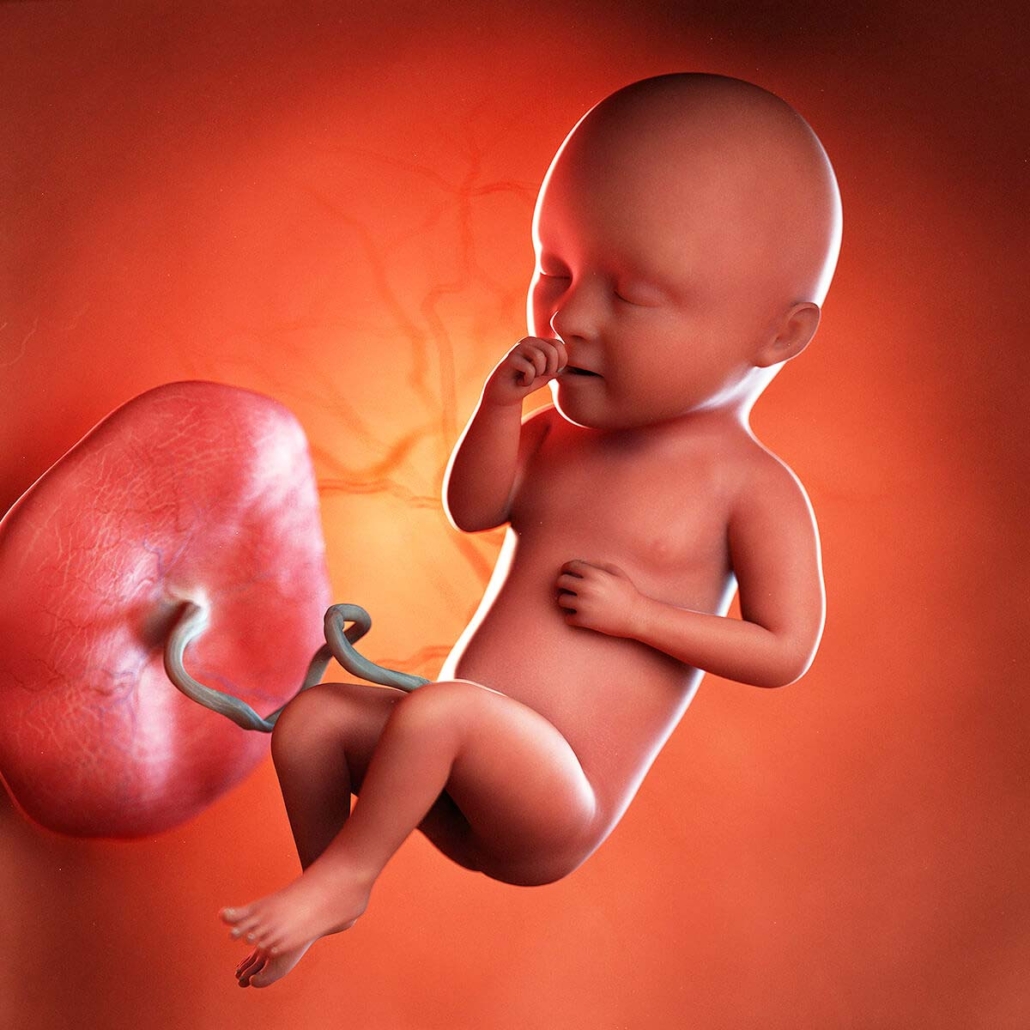
Some of the same discomforts you had in your second trimester will continue. Plus, many women find breathing difficult and notice they have to go to the bathroom even more often. This is because the baby is getting bigger and it is putting more pressure on your organs. Your baby will open his or her eyes, gain more weight, and prepare for delivery.
- 28: Baby’s eyes partially open
- 29: Baby kicks and stretches
- 30: Baby’s hair grows
- 31: Baby’s rapid weight gain begins
- 32: Baby practices breathing
- 33: Baby detects light
- 34: Baby’s fingernails grow
- 35: Baby’s skin is smooth
- 36: Baby takes up most of the amniotic sac
- 37: Baby might turn head down
- 38: Baby’s toenails grow
- 39: Baby’s chest is prominent
- 40: Your due date arrives
As you near your due date, your cervix becomes thinner and softer (called effacing). This is a normal, natural process that helps the birth canal (vagina) to open during the birthing process. Your doctor will check your progress with a vaginal exam as you near your due date. Get excited as the final countdown has begun.
Don’t be alarmed if your due date comes and goes with no signs of labor starting. Your due date is simply a calculated estimate of when your pregnancy will be 40 weeks. It does not estimate when your baby will arrive. It’s normal to give birth before or after your due date.
Disclaimer
The information on stages of pregnancy, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Preferences:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth
Pregnancy Fatigue
/0 Comments/in Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Personal, Pregnancy /by Rachel MataPregnancy Fatigue
Fatigue during pregnancy is very common. Some women may feel exhausted throughout their pregnancy, while some may hardly feel tired at all. One of the first signs of pregnancy is fatigue. Fatigue can begin in the very first weeks of pregnancy. It’s common to feel tired, or even exhausted, during pregnancy. Hormonal changes taking place in your body at this time can make you feel nauseous and emotional – affecting your body, mood, and sleep. Although experience with fatigue tends to vary, most women will feel more tired than usual during their pregnancy, and it is most common during the first trimester. It tends to go away during the second trimester, but will usually return in the third trimester.
What causes Pregnancy Fatigue?
It’s common to feel tired, or even exhausted, during pregnancy, especially in the first 12 weeks. Hormonal changes at this time can make you feel tired, nauseous, and emotional. The only answer is to rest as much as possible.
Causes of pregnancy fatigue for the first trimester:
- Building the placenta
- Your hormones
- Increased blood supply.
- Other physical changes
By the end of the first trimester, your body will have completed the enormous task that saps your body of energy on manufacturing the placenta and grown a bit more used to the hormonal and emotional changes that have occurred, which means the second trimester is usually a time of renewed energy levels.
During your second trimester, there is a good chance your energy level will increase and you will start to feel more like your old self. The second trimester is often called “The Happy Trimester.” Fatigue during pregnancy is still possible during the second trimester.
Causes of pregnancy fatigue for the third trimester:
- Your growing baby bump
- Pregnancy insomnia and other symptoms
- The stress of having a baby
- Multi-tasking
During the third trimester, you will most likely begin to feel tired again. At this point you will be carrying extra weight from the baby, maybe having trouble sleeping, and dealing with pregnancy demands.
Coping tips for Pregnancy Fatigue
- Make sure you allow yourself to get enough bed rest during the times you feel fatigued
- Eat healthy meals and stay hydrated. Try to look after your physical health by eating a healthy diet, and doing some gentle exercise. Eating nutritious meals will go a long way toward supporting your energy levels. Make sure you get enough iron, protein, and calories. Fatigue can become worse if you are not getting the proper nutrients. Make sure you stay hydrated during your pregnancy.
- Take time to exercise, if you incorporate moderate activity, such as a 30-minute walk, this will actually make you feel more energized. Exercise is beneficial in pregnancy unless your healthcare provider has advised otherwise.
Pregnancy can be a tiring experience, both emotionally and physically. It’s important to remember. You are not alone. Know that all of these pregnancy conditions are manageable and treatable, but you need to keep the communication lines open with your doctor.
Have a Happy, Healthy Pregnancy
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Exercising During Pregnancy
/0 Comments/in Health and wellness tip, Pegnancy tips, Pregnancy, Pregnancy Problem /by Rachel MataExercising During Pregnancy
All women who are pregnant without complications should be encouraged to keep up their normal daily physical activity or strength-conditioning exercises as part of a healthy lifestyle during their pregnancy. Pregnancy might seem like the perfect time to sit back and relax. You likely feel more tired than usual, and your back might ache from carrying extra weight. Exercise is not dangerous for your baby. There is some evidence that active women are less likely to experience problems in later pregnancy and labor. The more active and fit you are during pregnancy, the easier it will be for you to adapt to your changing shape and weight gain. Maintaining a regular exercise routine throughout your pregnancy can help you stay healthy and feel your best. It will also help you to cope with labor and get back into shape after the birth.
Who Should Not Exercise During Pregnancy?
For those that have medical problems, such as asthma, heart disease, diabetes, low placenta, bleeding or spotting, previous premature births, or a history of early labor, exercise may not be advisable.
Talk with your doctor before beginning an exercise program. They can also give you personal exercise guidelines, based on your medical history.
What Exercises Are Safe During Pregnancy?
Most exercises are safe to perform during pregnancy, as long as you exercise with caution and do not overdo it. Do not exhaust yourself. You may need to slow down as your pregnancy progresses.
- Dancing
- Swimming
- Water aerobics
- Yoga, stretching, and other floor exercises
- Pilates
- Biking
- Brisk walking
- Indoor stationary cycling
- pregnancy exercise classes
As a general rule, you should be able to hold a conversation as you exercise when pregnant. If you become breathless as you talk, then you’re probably exercising too strenuously.
Exercise tips during pregnancy
If you have been cleared to exercise, and you participated in physical activity before you were pregnant, it is recommended that you:
- Always warm up before exercising, and cool down afterward
- At least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity, try to keep active on a daily basis
- Listen to your body. Let your body be your guide.
- If you are healthy and you are not experiencing complications in your pregnancy, continue this level, or until it becomes uncomfortable for you to do so.
- Drink plenty of water and other fluids
- Try swimming because the water will support your increased weight.
- Consult and be guided by your doctor, physiotherapist, or healthcare professional.
Benefits of exercise during pregnancy
- Reduce backaches, constipation, bloating, and swelling
- Boost your mood and energy levels
- Help you sleep better
- Prevent excess weight gain
- Promote muscle tone, strength, and endurance
- Decreased risk of pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and pregnancy-induced hypertension
- Faster recuperation after labor
- Prevention and management of urinary incontinence
- Improved circulation
- Lower risk of gestational diabetes
- Shortened labor
- Reduced risk of having a C-section
Exercises to avoid while pregnant
- abdominal trauma or pressure; such as weightlifting
- Activities where falling is likely (such as skiing and horseback riding).
- extreme balance, coordination, and agility; such as gymnastics
- significant changes in pressure – such as SCUBA diving
- heavy lifting
- wide squats or lunges.
- Holding your breath during any activity.
- Activities that require extensive jumping, hopping, skipping, bouncing, or running.
- Deep Knee bends, full sit-ups, double leg raises, and straight-leg toe touches.
- Waist-twisting movements while standing.
- Heavy exercise spurts followed by long periods of no activity.
- Exercise in hot, humid weather.
Warning signs when exercising during pregnancy
Stop exercising and consult your health care provider if you:
- Feel chest pain
- Have a headache
- dizziness or feeling faint
- heart palpitations
- chest pain
- swelling of the face, hands, or feet
- calf pain or swelling
- vaginal bleeding
- contractions
- deep back, pubic or pelvic pain
- cramping in the lower abdomen
- an unusual change in your baby’s movements
- amniotic fluid leakage
- unusual shortness of breath
- excessive fatigue
- muscle weakness
Regular exercise can help you cope with the physical changes of pregnancy and build stamina for the challenges ahead. If you haven’t been exercising regularly, use pregnancy as your motivation to begin. If you’re not sure whether a particular activity is safe during pregnancy, check with your healthcare professional. Always talk to your doctor before beginning any exercise program. Once you’re ready to get going.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
References:
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/exercising-pregnancy.html