Is There a Device to Measure Blood Oxygen?
Is There a Device to Measure Blood Oxygen? A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s health-conscious world, monitoring vital signs has become a paramount concern for many. Among these vital signs, blood oxygen levels emerge as a crucial indicator of our respiratory and overall health. Consequently, this leads to a pressing question that many health enthusiasts and patients alike find themselves asking: “Is there a device to measure blood oxygen?” Fortunately, the answer is a resounding yes. Moreover, this comprehensive guide will introduce you to the wonders of pulse oximetry, the technology behind these life-saving gadgets, providing an insightful exploration into how they work and their significance in our daily lives
What is Pulse Oximetry?
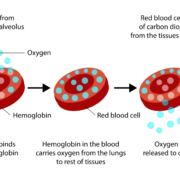
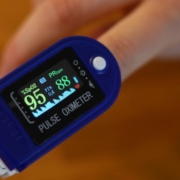
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method used to measure the oxygen saturation level of the blood. Importantly, this technology offers the convenience of real-time monitoring without the need for cumbersome blood samples. So, how does it work? Simply put, a pulse oximeter utilizes light beams to estimate the oxygen saturation in your blood and your pulse rate. Specifically, the device typically clips onto a part of the body, often a finger, toe, or earlobe. It then uses red and infrared light to measure how much oxygen is in your blood based on how the light passes through your finger. This approach allows for an efficient and painless way to monitor vital health indicators.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Oxygen Levels
Monitoring blood oxygen levels can be vital for individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions, athletes, and anyone interested in maintaining optimal health. Generally, normal blood oxygen saturation levels usually range from 95% to 100%. Consequently, values below 95% may indicate a need for medical evaluation, as insufficient oxygenation can lead to severe health issues. Specifically, this situation could result in hypoxemia, which demands prompt medical attention to prevent further complications.
Types of Pulse Oximeters
- Fingertip Pulse Oximeters: These portable devices are the most common and are widely used at home for personal monitoring. They are compact, easy to use, and provide quick readings.
- Handheld Pulse Oximeters: Often found in medical settings, these devices come with a probe that is attached to the patient, offering more detailed monitoring capabilities.
- Wearable Pulse Oximeters: Designed for continuous monitoring, these oximeters can be worn on the wrist and are ideal for patients needing constant observation without hospitalization.

How to Use a Pulse Oximeter
Using a pulse oximeter is straightforward:
- Turn on the device and place it on your finger, toe, or earlobe.
- Wait a few seconds for the device to calculate the reading.
- Read the display, which will show your oxygen saturation level (SpO2) and pulse rate.
Choosing the Right Pulse Oximeter
When selecting a pulse oximeter, consider the following:
- Accuracy: Look for devices with an accuracy of ±2% for SpO2 readings.
- Ease of Use: The device should be user-friendly, with a clear display and simple operation.
- Durability and Portability: Choose a robust device if you plan to carry it frequently.
- Price: Prices vary, so select one that fits your needs and budget.
Conclusion: Empowering Health with Technology
In answering the question, “Is there a device to measure blood oxygen?” we’ve uncovered the critical role pulse oximeters play in health monitoring. Importantly, whether for personal health management, athletic performance, or medical needs, these devices offer an easy and efficient way to keep a close eye on your vital signs. It’s essential to remember, while pulse oximeters provide valuable insights, they are not substitutes for professional medical advice. Therefore, always consult with a healthcare provider for concerns about your health and well-being.
Moreover, as technology continues to evolve, the integration of such devices into our daily lives emphasizes the importance of staying informed and proactive about our health. By understanding and utilizing tools like pulse oximeters, we significantly empower ourselves to lead healthier, more informed lives. This proactive approach not only enhances our ability to monitor our health but also encourages a culture of wellness and informed decision-making.
Check out the latest pulse oximeters to find the device that best suits your needs, and take a step today towards a healthier tomorrow.
External resources:
- American Lung Association. Provides a wealth of information on how blood oxygen levels affect lung health and offers guidance on managing respiratory conditions. Visit their website at American Lung Association.
- Mayo Clinic. Offers detailed insights into the importance of monitoring your blood oxygen levels and how it can signal various health conditions. Explore more at Mayo Clinic.
- Consumer Reports. For those in the market for a pulse oximeter, Consumer Reports offers unbiased reviews and buying guides to help you choose the right product. Check their recommendations at Consumer Reports.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). Provides scientific articles and research studies on pulse oximetry, explaining the technology, its applications, and its limitations. Read their publications at NIH.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Offers guidelines and educational materials on preventing respiratory illnesses and how monitoring blood oxygen levels can be a critical part of managing health. Visit CDC for more information.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.