Blood Oxygen Level; all you need to know:
What is Blood Oxygen Level?
Blood oxygen level measures the oxygen circulating in your blood. Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s parts, indicating how effectively the body moves oxygen from the lungs to the cells. This level is crucial for health.
Measuring Your Blood Oxygen Level
You can measure your blood oxygen level in two ways: through an arterial blood gas test or a pulse oximeter. The arterial blood gas test, a blood test, accurately measures your blood’s oxygen level and checks your blood’s pH balance. Although accurate, this test is invasive. On the other hand, a pulse oximeter offers a noninvasive estimate by sending infrared light into capillaries in your finger, toe, or earlobe and measuring the reflected light. This method provides a reading of your blood’s oxygen saturation (SpO2 level) but has a 2 percent error margin. Despite being slightly less precise, doctors prefer it for its convenience in offering quick readings.
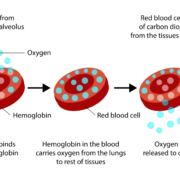
How Blood Becomes Oxygenated
Oxygen saturation in blood starts in the lungs’ alveoli, tiny air sacs responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules with the bloodstream. The Oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the blood, which then delivers oxygen to tissues while carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs. Ideally, oxygen levels in your blood depend on several factors, including the amount of inhaled oxygen, alveoli efficiency, hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells, and hemoglobin’s oxygen attraction. Usually, hemoglobin carries enough oxygen for the body’s needs, but certain diseases can impair its ability to bind oxygen.
Low Blood Oxygen Levels
An oxygen saturation level below 95% is generally abnormal, and below 90% signals an emergency requiring oxygen therapy. The brain, highly sensitive to hypoxia, can suffer cell death within five minutes of oxygen deprivation, leading to serious outcomes like coma, seizures, and brain death if prolonged. Identifying and addressing the cause of low oxygen saturation is crucial. Conditions like COPD and asthma typically result from inadequate air exchange in the lungs and alveoli. Treatments may include oxygen therapy, steroids, or bronchodilators to open the airways.
Treatment
For low blood oxygen levels, treatment options include supplemental oxygen, available in-office or for home use, though some devices require a prescription. Lifestyle changes, like a healthy diet, can also improve oxygen levels and overall health. Since iron deficiency often leads to low oxygen saturation, consuming iron-rich foods such as meat, fish, kidney beans, lentils, and cashew nuts is beneficial.
Disclaimer
This information aims to enhance understanding and knowledge of health topics and is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions about a medical condition or treatment. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it based on what you have read on this website.
References: